Tree Planting Guidelines
Introduction
Tree planting is more than just an act of gardening; it’s a powerful way to contribute to the health of our planet and our communities. Trees offer countless benefits, from improving air quality to providing shade and enhancing the beauty of our surroundings. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to beautify your yard or a community leader aiming to green your neighborhood, understanding the guidelines for tree planting is essential for success.

Choosing the Right Tree
Choosing the right tree is the first and most crucial step in tree planting. You need to consider your local climate and soil conditions to ensure the tree will thrive. Also, think about the purpose of the tree—whether it’s for shade, fruit, or aesthetic appeal. Native species are often the best choice as they are adapted to the local environment and support local wildlife.
Assessing Local Climate and Soil
Before you head to the nursery, take some time to assess your local climate and soil. Different trees have different requirements, and matching the tree to your environment will give it the best chance of thriving.
Considering the Purpose of the Tree
Are you planting a tree for shade, to attract wildlife, or for its fruit? Knowing the primary purpose of your tree will help narrow down your choices and ensure you select a tree that meets your needs.
Native vs. Non-Native Species
While non-native species can be appealing, native species usually require less maintenance and provide better support for local ecosystems. They are adapted to the local climate and soil, which often makes them more resilient and easier to care for.
Selecting the Planting Site
Once you’ve chosen your tree, the next step is to select the right spot for planting. The site should provide adequate sunlight, have good soil quality, and enough space for the tree to grow.
Evaluating Sunlight Exposure
Most trees need plenty of sunlight to grow, so choose a spot that gets at least six hours of direct sunlight each day.
Checking Soil Quality
Good soil is vital for tree health. Test your soil to ensure it has the right pH and nutrient levels for the tree you’ve chosen. To achieve optimal growing conditions, it might be necessary to improve the soil.
Ensuring Adequate Space
Consider the mature size of the tree. Make sure there’s enough space for the roots to expand and for the tree to grow to its full height without interfering with buildings or power lines.

Preparing the Planting Site
Preparation is key to successful tree planting. Clear the area of weeds and debris, prepare the soil, and dig a hole that’s the right size for the tree’s root ball.
Clearing the Area
Clear the planting area of any grass, weeds, or debris. This reduces competition for nutrients and water.
Soil Preparation
Dig the soil down to a depth of roughly 12 inches. This helps the roots penetrate and establish themselves more easily.
Digging the Right-Sized Hole
Make the hole twice as wide as the root ball, but not deeper. Planting the tree too deep can cause root rot and other issues.
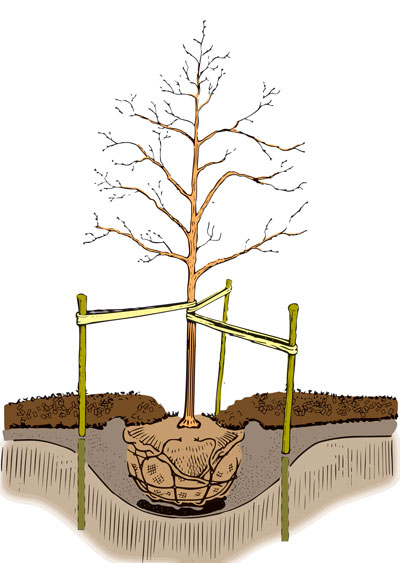
Planting the Tree
Now comes the actual planting. Handle the tree carefully to avoid damaging the roots, place it in the hole, and backfill with soil.
Handling the Tree Safely
When transporting and handling the tree, be gentle to avoid breaking the roots or damaging the trunk.
Placing the Tree in the Hole
Set the tree in the hole, making sure it’s straight and the root collar (where the roots meet the trunk) is level with the ground.
Backfilling and Watering
Fill the hole with soil, gently pressing it down to eliminate any air pockets. Water the tree thoroughly to help settle the soil and eliminate air pockets.
Post-Planting Care
Taking care of your tree after planting is crucial for its survival. Mulch around the tree, establish a watering schedule, and protect it from pests.
Mulching Around the Tree
Spread a layer of mulch around the tree’s base. Mulch aids in moisture retention, weed suppression, and soil temperature regulation.
Watering Schedule
Newly planted trees need consistent watering. Water deeply once a week, more often in hot, dry weather. Be careful not to overwater.
Protecting the Tree from Pests
Use tree guards or protective wraps to shield your tree from pests and animals. Regularly check for signs of disease or insect infestation.

Long-Term Tree Care
Long-term care includes pruning, fertilizing, and monitoring the health of your tree to ensure it continues to thrive.
Pruning Techniques
Prune your tree to remove dead or diseased branches, promote healthy growth, and shape it. The ideal time for pruning is during the late winter or early spring.
Fertilizing Needs
Depending on your soil quality, you may need to fertilize your tree. Use a slow-release fertilizer in the spring to provide essential nutrients.
Monitoring Tree Health
Regularly inspect your tree for signs of stress, disease, or pest problems. Early detection and treatment can prevent more serious issues.
Community Involvement in Tree Planting
Tree planting is a fantastic way to bring communities together. Organize events, educate your neighbors, and collaborate with local authorities to create greener spaces.
Organizing Community Tree Planting Events
Get your community involved by organizing tree planting events. These events can foster a sense of community and make a significant impact on the local environment.
Educating the Community
Raise awareness about the benefits of tree planting. Hold workshops and distribute information to educate people about proper tree planting and care.
Collaborating with Local Authorities
Work with local government and organizations to secure funding, resources, and permissions for large-scale planting projects.
Benefits of Urban Tree Planting
Urban tree planting has numerous benefits, including improving air quality, reducing heat islands, and enhancing the aesthetic value of cities.
Improving Air Quality
Trees absorb pollutants and produce oxygen, making urban areas healthier for residents.
Reducing Urban Heat Islands
Enhancing Aesthetic Value
Well-placed trees can transform the look of a neighborhood, making it more inviting and increasing property values.
Challenges in Tree Planting
Despite the benefits, tree planting comes with challenges such as soil compaction, limited space, and potential vandalism.
Overcoming Soil Compaction
In urban areas, soil compaction can be a major issue. Use techniques like aeration and adding organic matter to improve soil structure.
Dealing with Limited Space in Urban Areas
Space can be limited in cities. Choose compact tree species or consider vertical planting solutions to maximize space.
Trees provide shade and release moisture into the air, which can significantly reduce the temperature in urban areas.